What is OCSP?
- OCSP is a method used to determine the status of a public key certificate.
- The acronym “OCSP” stands for “Open Certificate Status Protocol”.
- This method is used by many web browsers to check revocation status of certificates used for HTTPS connections.
The Purpose of OSCP
Preventing revoked certificate use by verifying the revocation status of public key certificates.
Overview
During a secure connection between a web browser and a web server, some information is shared. Part of that information is a public key certificate. That public key certificate may or may not be revoked (bad). OCSP checks the status of that “key”.
In the image below we see a key being shared between a web browser and a web server. The browser can then take this “key” and check with a trusted OCSP server to see the keys’ status.
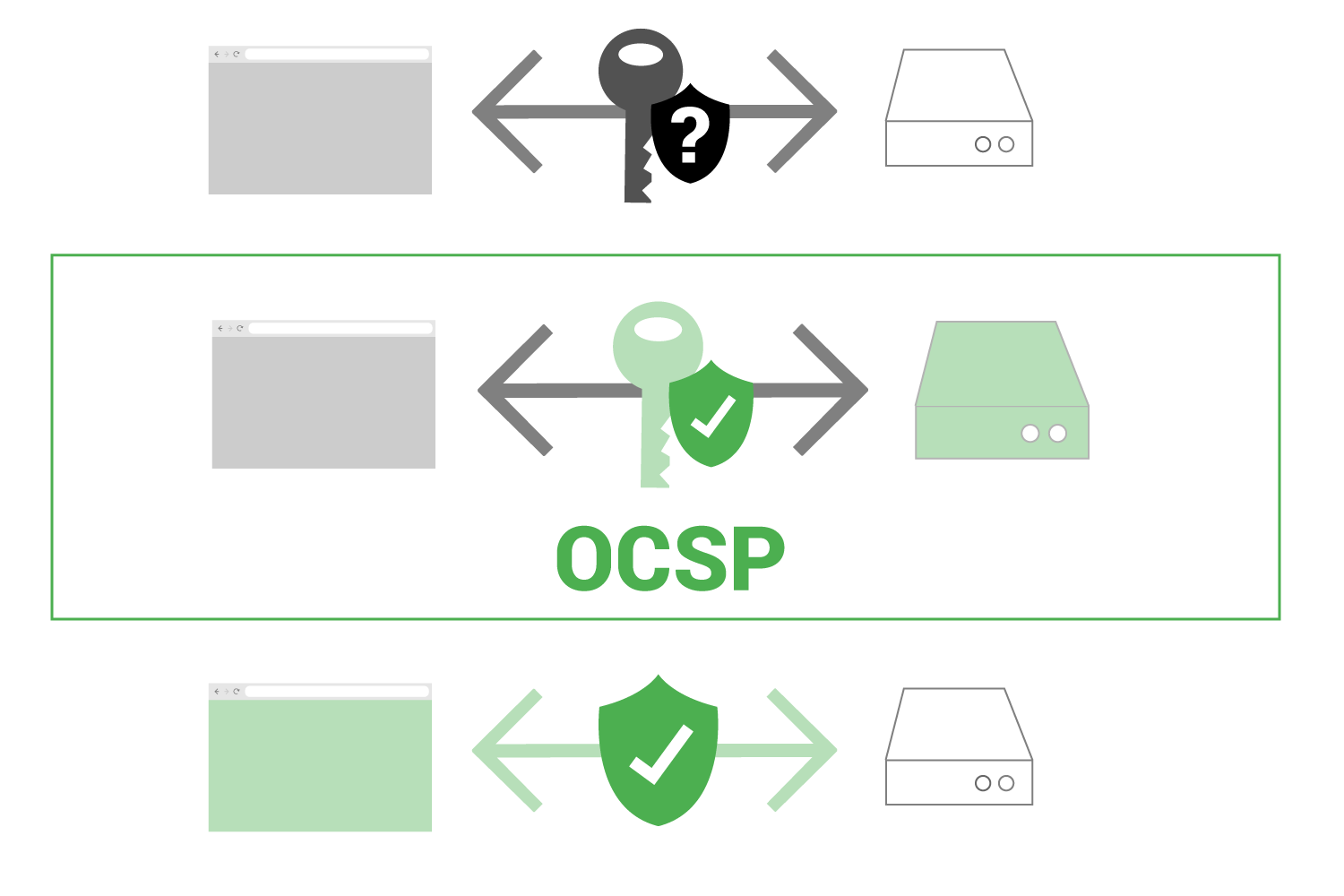
If the key status is good, the web browser can then establish a secure connection with the original web browser, confident that the key is valid.
Imagine there is a certificate authority and for some reason a group of their certificates are compromised, meaning they are no longer safe to use. In this scenario, unless the web browser checked the status of the public key certificate first, it could be using a unsafe certificate.
OCSP allows that status check to occur.
OCSP Server (Responder)
An OCSP server (often referred to as a responder) is a trusted server maintained by a Certificate Authority which responds to queries.
In order to see a certificate’s status, a web browser makes a query.
That query is sent is an OCSP server.
Query / Response
The query is basically a web browser asking… “What is the status of this certificate?”
The response provided by the OCSP server is basically saying … “This certificate is valid according to my records.”
OSCP server responses
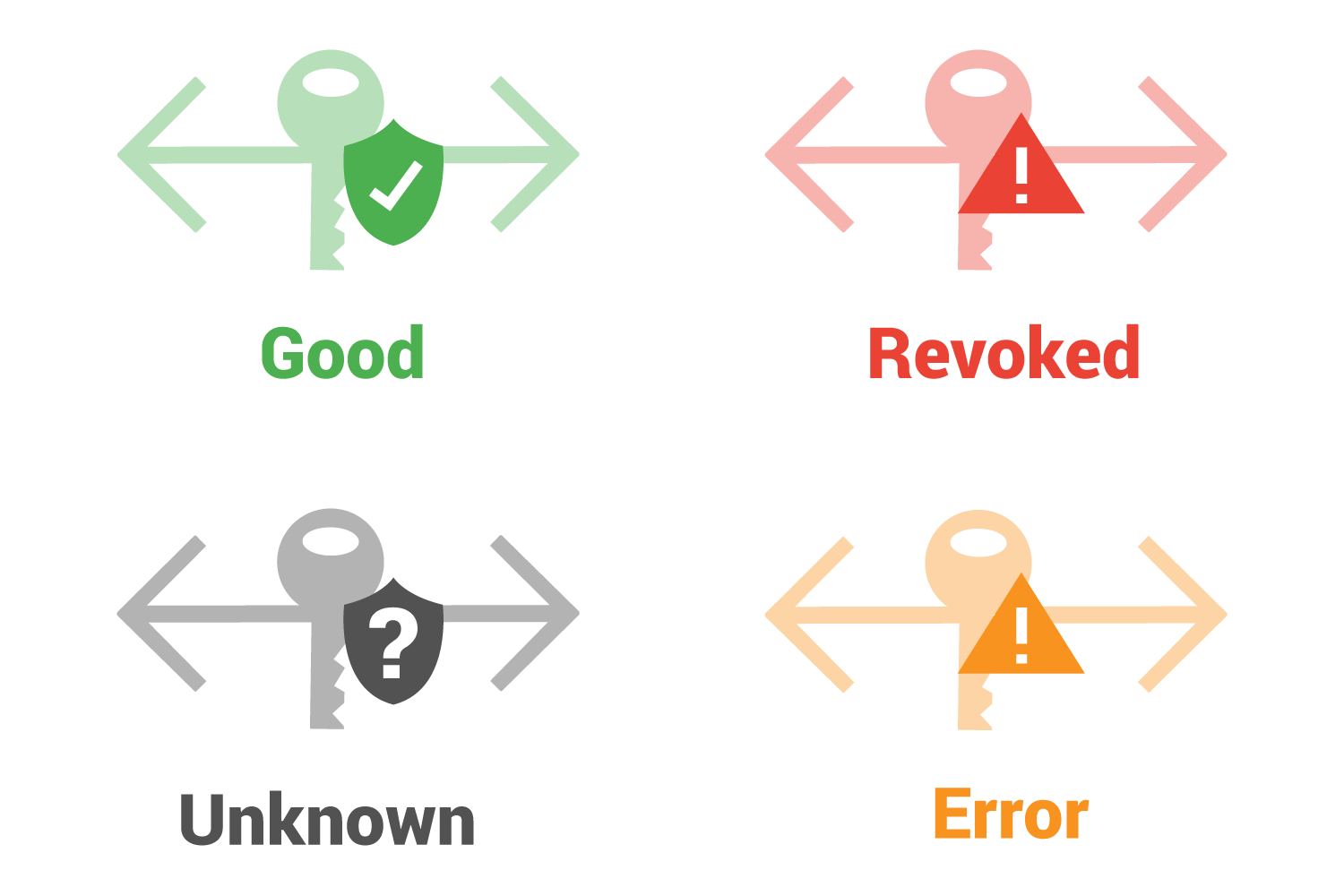
There are four general responses: Good, Revoked, Unknown, and Error.
What browsers do with OCSP responses
Web browsers use the OCSP response to determine if and how to establish a secure connection.
So let’s look at a situation where a certificate is revoked (bad).
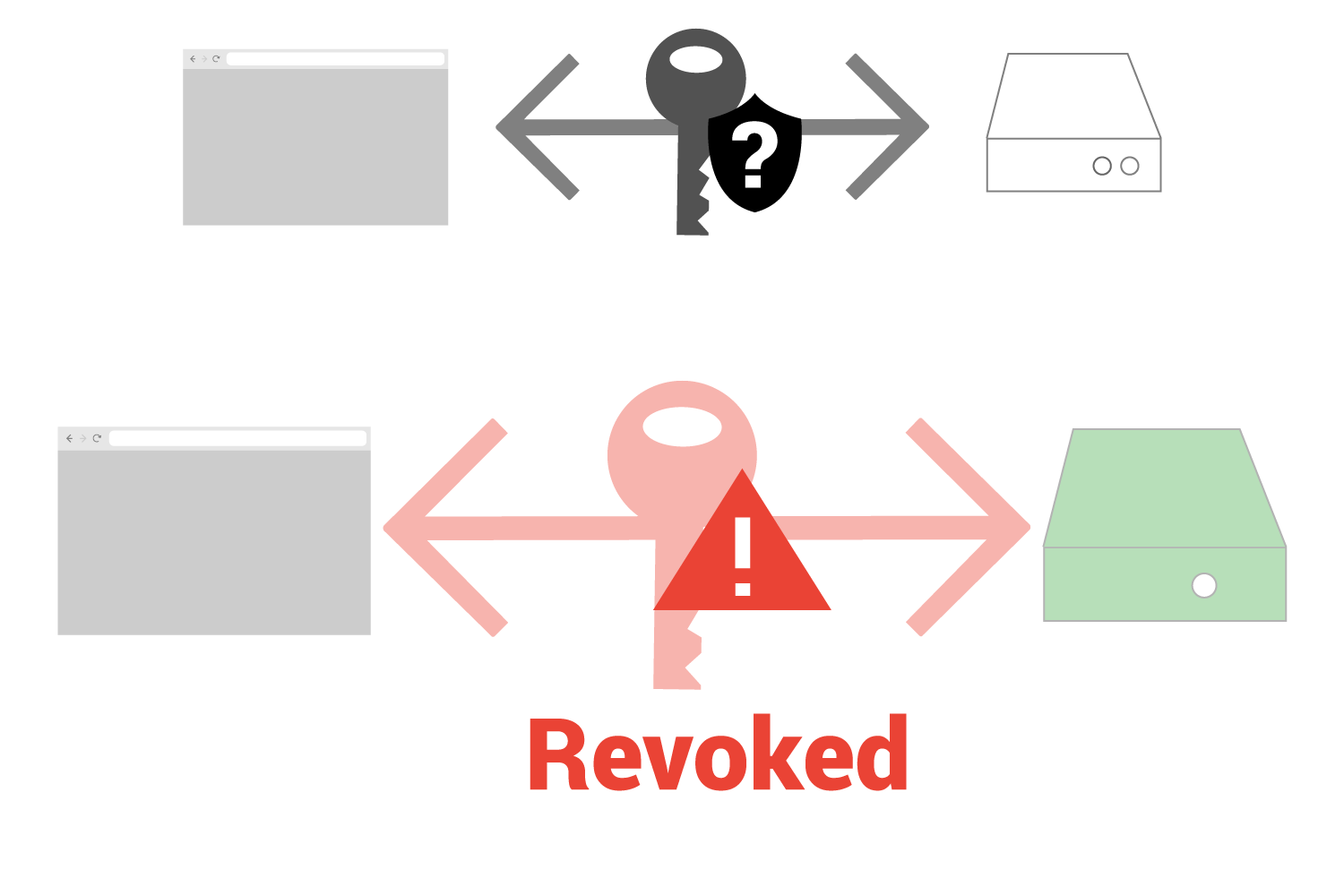
In this case, the web browser has started a connection with a web server and received a key. It then uses OCSP and discovers that the certificate is revoked.
What does the browser do now?
Each major browser decides for itself what to do in this scenario. The browsers may report an error status, warn users, end the connection, or continue with the connection in a different manner. If that answer doesn’t seem clear, it is only because browsers themselves are always experimenting. Chrome, Firefox, and Edge browsers all have varied their process over the past several years.
OCSP Performance considerations
Using OCSP has one major affect on page speed performance. It requires a new connection to the OCSP server which requires time. Even if the OCSP servers are running flawlessly, that will still add time to how long it takes a visitor to see a webpage. In other scenarios, such as a less performant (slow) OCSP server, this can add significant time to the process of displaying a webpage.
Privacy considerations
OCSP also has a big privacy issue. If your web browser is visiting a OCSP server every time you go to a new page, that can mean that the OCSP server could theoretically have a record of every webpage you visit.
OCSP Stapling
The answer to both the performance and privacy issues is called OCSP stapling.
Learn more about OCSP Stapling here.
See more of our HTTPS articles

 Table of Contents
Table of Contents